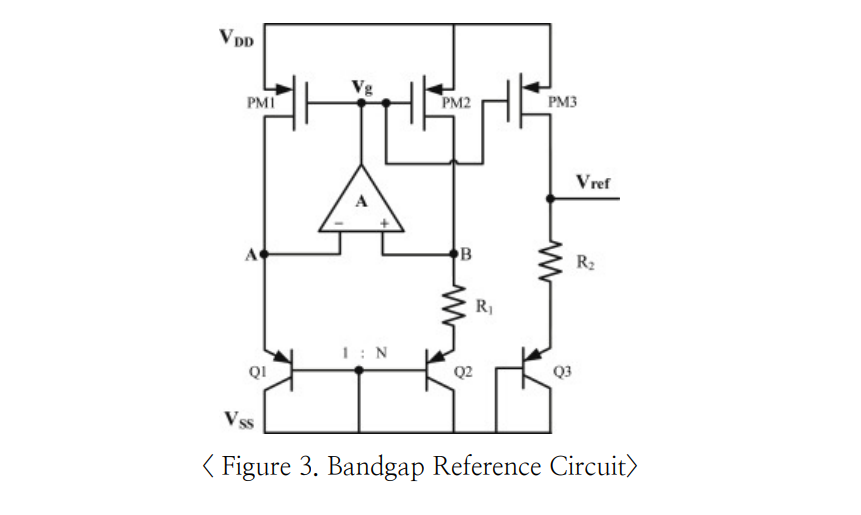
Why do circuits need accurate references? The first is to provide stable biasing of the analog circuit, and the second is that the reference should be robust on PVT variation. A voltage formed in reference is used for almost all blocks of ATOP, such as CDS, RDV, DBS, DBR, RMP, etc., so it is essential to design an accurate voltage reference for accurate image processing. BGR utilizes a method of creating an Invariant Reference according to the temperature change by combining the CTAT Component, which produces negative numbers when differentiated by temperature, and the PTAT Component, which shows positive numbers.
The well-known error sources for BGR circuits include Mismatch, Op-amp Offset, and Op-amp Finite DC Gain. The most focused project in this block is to improve the distribution of this Bandgap Reference. Even if the reference voltage used for each block of CIS is slightly distorted, the code changes, which can degrade the noise or quality of the picture. No matter how little variation is in Voltage and Temperature, variations according to the process, i.e., process dispersion, may cause an error of up to +/20 mV, which varies depending on the resolution, the following code error may occur considering 19-bit ADC and Normal Voltage 2.5V: 20 X 10^-3 / 2.5 X 2^10 = 8.2 Codes, which can lead to enormous error. Therefore, it is most important to reduce the process dispersion. In this project, a total of two process dispersion mitigation technologies were used. First, the Standard-Cell-based sizing design, that is, sizing was designed as an integer multiple of Logic Size in the designed process. Second, the dispersion was reduced by increasing the Device Size.
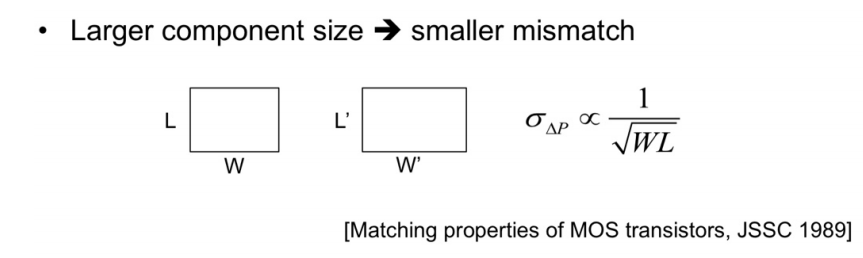
Since the dispersion is inversely proportional to the area (WL) of the component as shown in the following equation, the dispersion may be reduced by increasing the sizing. With the same principle, the dispersion can be reduced by increasing the spacing of the layout of each component. The reason why this method was not used in the field is that it is expected that the value made in consideration of various trade-offs such as power or chip footprint limitations as the increased area was included in the mass product, and this project designed the Bandgap Reference in the above direction. 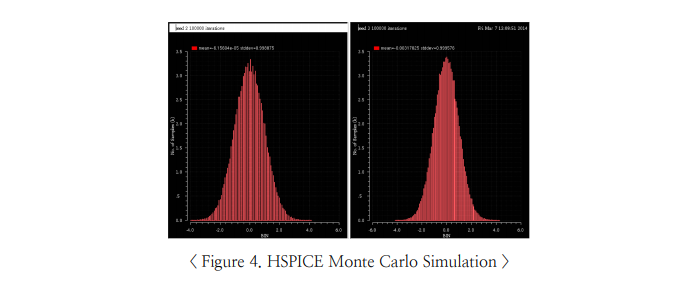
The results can be confirmed through Monte Carlo Simulation, which can check the process dispersion. As a result, it was confirmed that the dispersion of about 14.6% in the high temperature and about 16.8% in the low temperature can be reduced.
- Please understand that detailed simulation methods or results cannot be prepared due to internal security regulations.